Early detection of respiratory diseases: the key to better health
Introduction
Respiratory diseases are among the leading causes of illness and death worldwide. Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary fibrosis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications. Early detection of these diseases is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention, management, and prevention of disease progression. This article explores the importance of early detection of respiratory diseases, with a focus on spirometry — a simple, non-invasive test that plays a pivotal role in diagnosing these conditions.
The burden of respiratory diseases in Europe
Respiratory diseases pose a significant health burden in Europe. According to the European Lung Foundation, lung diseases account for about 20% of all deaths in the European region. The most common conditions include asthma, COPD, lung cancer, and respiratory infections. Factors such as air pollution, smoking, occupational hazards, and genetic predispositions contribute to the high prevalence of these conditions.
In many cases, respiratory diseases develop slowly, with symptoms that can be easily overlooked or mistaken for less serious issues. Unfortunately, by the time these conditions are diagnosed, the disease may have progressed to a more advanced stage, making treatment more difficult and less effective. This highlights the need for early detection and regular monitoring of lung health, especially in individuals at higher risk.
Preventive measures for respiratory diseases
Preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing respiratory diseases and emphasize the importance of early detection:
- Smoking cessation programs: Quitting smoking is the most effective way to prevent respiratory diseases, and spirometry can be used to monitor lung health improvements after cessation.
- Environmental control and air quality: Reducing exposure to pollutants can lower the risk of respiratory diseases, and regular spirometry can help track lung function over time.
- Vaccination: Vaccines for diseases like pneumonia can prevent respiratory infections that may lead to chronic conditions.
- Regular health check-ups including spirometry: Incorporating spirometry into routine health check-ups, especially for high-risk individuals, can ensure early detection of respiratory diseases.
The importance of early detection
Early detection of respiratory diseases can significantly improve patient outcomes. When these conditions are identified in their early stages, treatment can be more effective, and patients have a better chance of maintaining their quality of life. Early detection also helps to prevent complications, reduce healthcare costs, and improve long-term prognosis.
Benefits of early detection include:
- Timely intervention: Early diagnosis allows for prompt treatment, which can slow disease progression, relieve symptoms, and improve overall health.
- Improved quality of life: Managing respiratory diseases from an early stage helps patients maintain their normal activities and reduces the impact of the disease on their daily lives.
- Cost savings: Early treatment and management of respiratory diseases can reduce the need for expensive hospitalizations and more intensive treatments later on.
- Prevention of complications: By detecting diseases early, patients can avoid serious complications such as respiratory failure, heart problems, and other related conditions.
- Personalized treatment plans: Early detection allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to the specific needs of each patient, leading to better outcomes.
Diagnostic methods for early detection of respiratory diseases
Diagnosing respiratory diseases early involves various tests and procedures, with spirometry being a key tool among them. However, a comprehensive approach often includes multiple diagnostic methods to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Spirometry
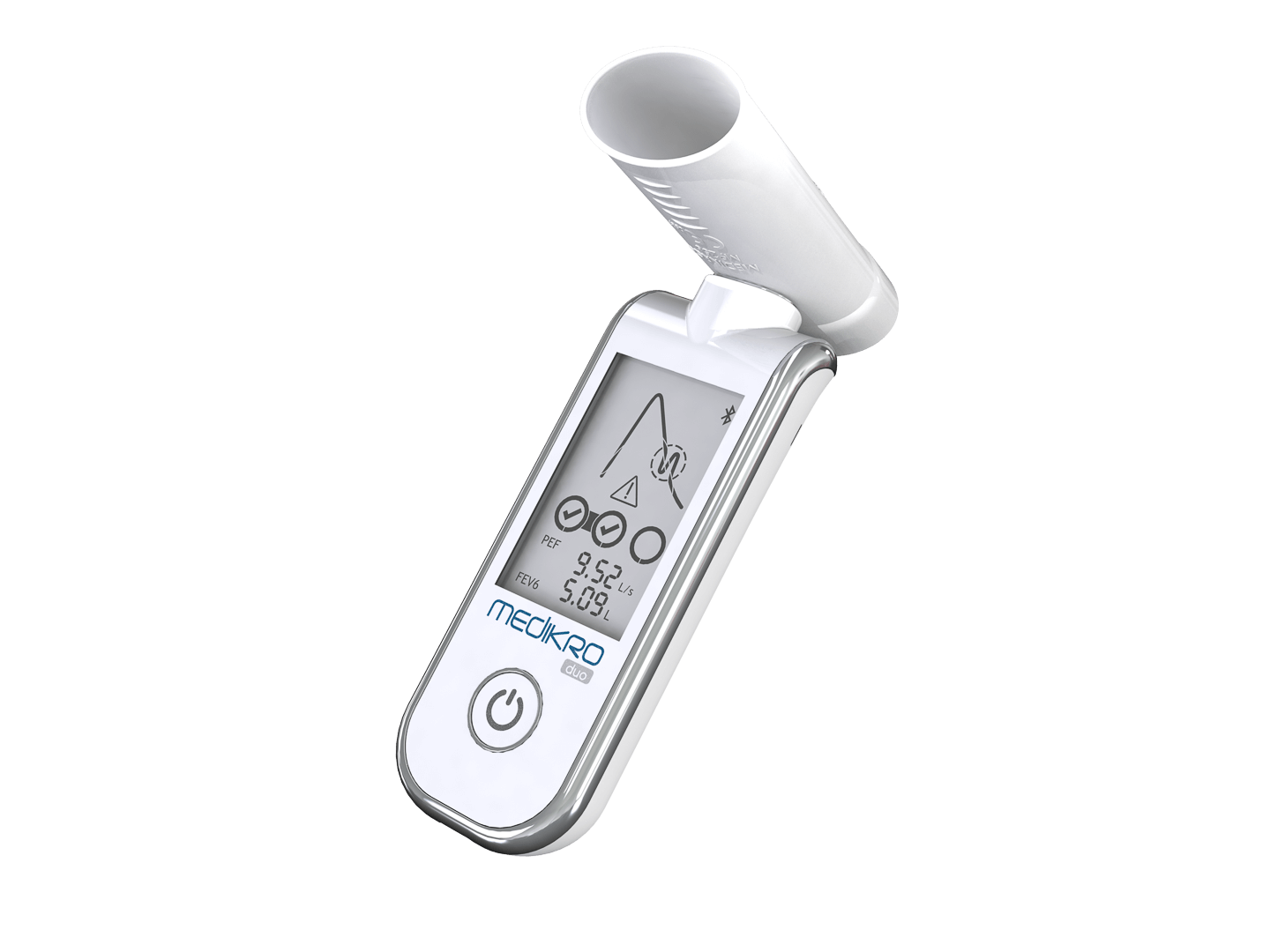
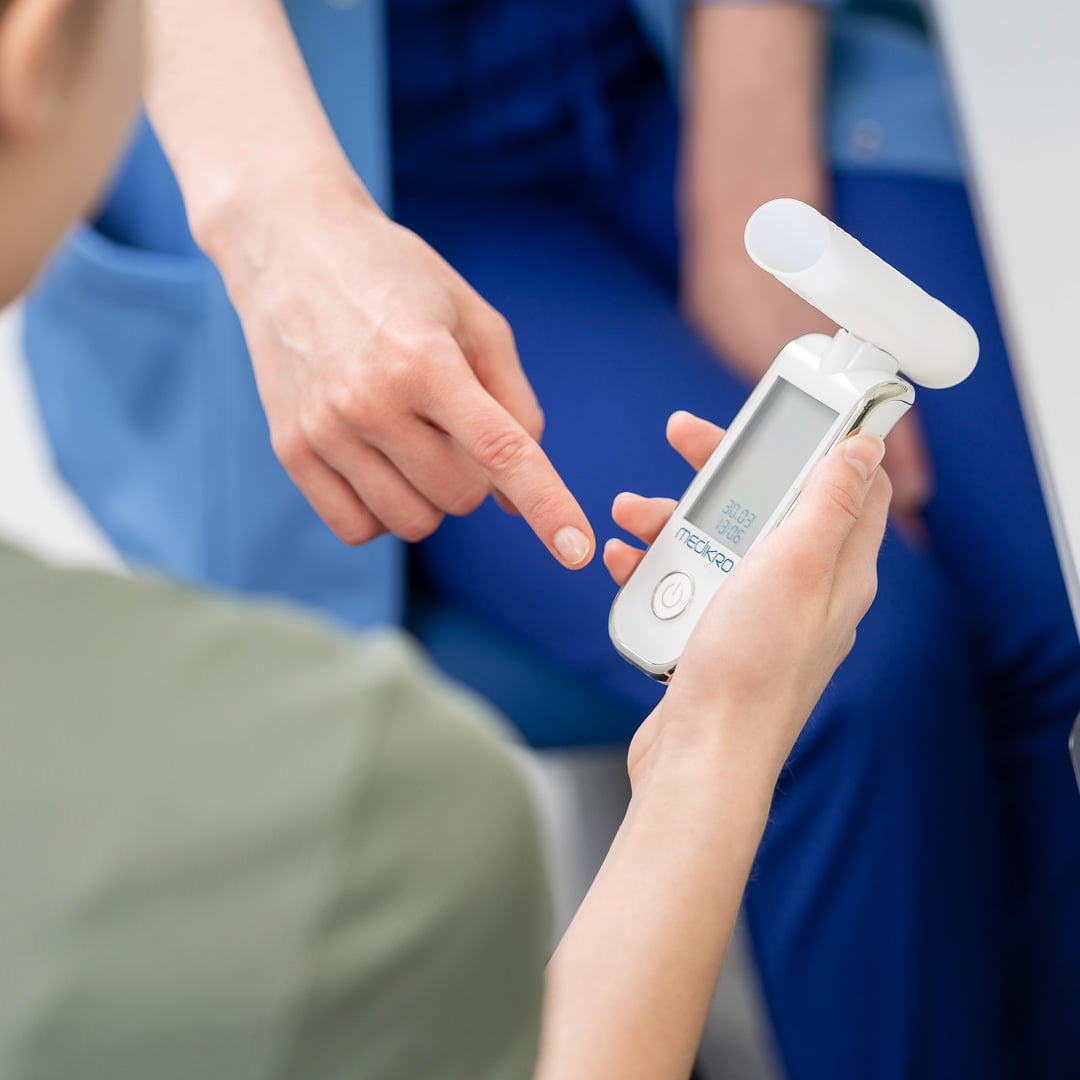
Spirometry is a fundamental test in respiratory diagnostics. It measures how much air a person can inhale and exhale, as well as how quickly they can exhale. Spirometry is particularly effective in diagnosing obstructive lung diseases, such as COPD and asthma, making it a cornerstone of respiratory diagnostics.

Spirometry is recommended for anyone experiencing symptoms of a respiratory disease, such as chronic cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, or frequent respiratory infections. It is also advisable for individuals at higher risk of respiratory diseases, including smokers, those with a history of lung diseases in the family, and people exposed to occupational hazards like dust, chemicals, or fumes.
During a spirometry test, the patient is asked to take a deep breath and then exhale as forcefully as possible into a mouthpiece connected to a spirometer. The spirometer records the amount of air exhaled and the speed of exhalation. The two primary measurements taken during spirometry are:
- Forced Vital Capacity (FVC): The total amount of air exhaled during the test.
- Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1): The amount of air exhaled in the first second of the test.
These measurements are compared to standard reference values based on the patient’s age, height, gender, and ethnicity. Abnormal results may indicate the presence of a respiratory disease, prompting further investigation or immediate intervention.
Imaging techniques
Imaging techniques like chest X-rays and CT scans provide detailed images of the lungs, allowing healthcare providers to identify abnormalities such as tumors, scarring, or inflammation. These imaging tools are essential for diagnosing conditions like lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis, where structural changes in the lungs are a primary concern.
Blood tests and biomarkers
Blood tests can detect markers of inflammation or infection that may indicate the presence of a respiratory disease. For example, elevated levels of certain proteins or white blood cells can suggest an ongoing inflammatory process in the lungs. Biomarkers in the blood can also help monitor the progression of respiratory diseases and the effectiveness of treatment.
Sputum analysis
Sputum analysis involves examining mucus or phlegm that is coughed up from the lungs. This test can help identify infections, such as bacterial pneumonia or tuberculosis, as well as abnormal cells that may indicate lung cancer. Sputum analysis is particularly useful in diagnosing infectious respiratory diseases and monitoring chronic conditions.
Genetic testing
Genetic testing can identify individuals at higher risk for certain hereditary respiratory diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Early identification of genetic predispositions allows for proactive management and intervention before the onset of symptoms.
Barriers to widespread use of spirometry and what we do to overcome it
Despite its benefits, spirometry is not as widely used in primary care as it could be. Barriers include a lack of training among healthcare providers, limited access to spirometry equipment, and insufficient awareness of the test’s importance among the general public. Addressing these challenges through education, training, and access to affordable devices is crucial for enhancing early detection efforts.
Medikro is committed to overcoming these barriers by providing high-quality, reliable spirometers that are easy to use in both clinical and primary care settings. Our initiatives include projects like the recent introduction of spirometry services in Tansen, Nepal, where we provided equipment and training to support healthcare providers in remote areas.
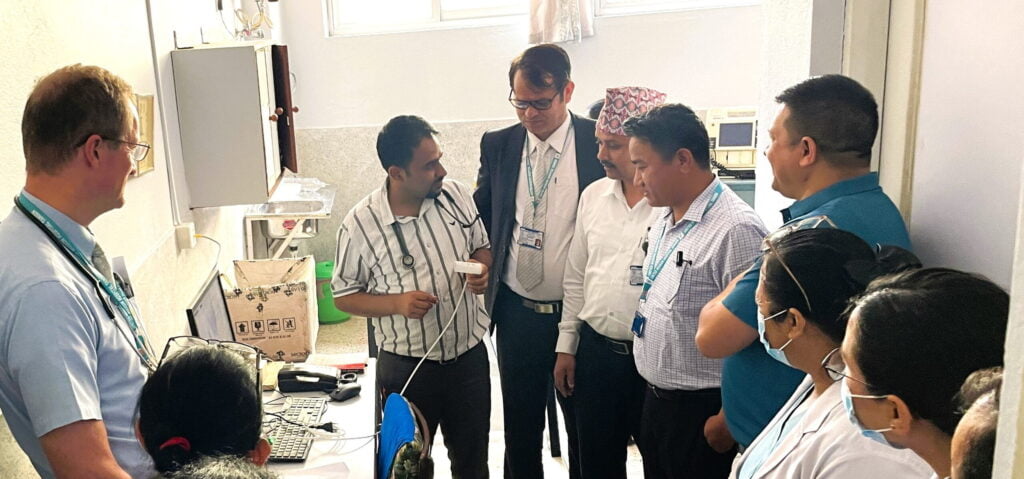

Additionally, we engage in community outreach to raise awareness about respiratory health. At the 14th GRAP Conference in Burgos, Spain, we supported free spirometry tests for local residents, demonstrating the value of early disease detection.
To further support primary care settings, Medikro offers one-to-one and group online training sessions for healthcare professionals. These sessions provide practical guidance on achieving accurate results with our equipment, and can be easily booked through our website.
Through these efforts, Medikro is breaking down the barriers to spirometry use, ensuring that more healthcare providers and patients benefit from early detection and management of respiratory diseases.
Conclusion
Early detection of respiratory diseases is essential for improving patient outcomes, reducing healthcare costs, and preventing complications. Spirometry is a key tool in this effort, enabling healthcare providers to diagnose conditions like asthma, COPD, and pulmonary fibrosis at an early stage. By making spirometry more accessible and raising awareness of its importance, we can ensure that more individuals receive the timely care they need to maintain their lung health.
Medikro is committed to supporting these efforts through the provision of high-quality spirometry equipment and ongoing education initiatives. Together, we can work towards a future where respiratory diseases are detected early and managed effectively, leading to better health outcomes for all.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
How does spirometry work, and why is it important?
Spirometry measures lung function by assessing the volume of air a person can exhale after a deep breath and the speed at which the air is exhaled. It is crucial for diagnosing conditions like COPD and asthma early, often before symptoms become apparent.
When should I have a spirometry test?
You should consider spirometry if you are a smoker, have a family history of respiratory diseases, or experience symptoms like shortness of breath, chronic cough, or wheezing. Regular testing is also recommended for individuals with known respiratory conditions.
Can spirometry detect all respiratory diseases?
While spirometry is highly effective for diagnosing obstructive lung diseases like COPD and asthma, it is less effective for detecting restrictive lung diseases or conditions that do not primarily affect airflow.
How does early spirometry affect treatment outcomes?
Early detection through spirometry allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve treatment outcomes, slow disease progression, and maintain a better quality of life.
What should I do if my spirometry results are abnormal?
If your spirometry results are abnormal, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation. Additional tests may be required to diagnose the specific condition and determine the best course of treatment.
How can I ensure access to spirometry in my community?
Advocate for spirometry in local healthcare settings, support public health initiatives that promote respiratory health, and educate others about the importance of early detection through spirometry.
This article has been reviewed by
Elina Kiviaho
Senior Biomedical Laboratory Scientist, Clinical Expert in Biomedical Analytics
Linkedin

More from the articles:
Cooperation that endures and evolves – Medikro and Savonia jointly build practice-oriented spirometry education
15.11.2025
Read moreCreating future professionals through collaboration – Medikro Spirometers in teaching at Oulu University of Applied Sciences
21.10.2025
Read more